Publications
Oredered in reversed chronological order.
2024
-
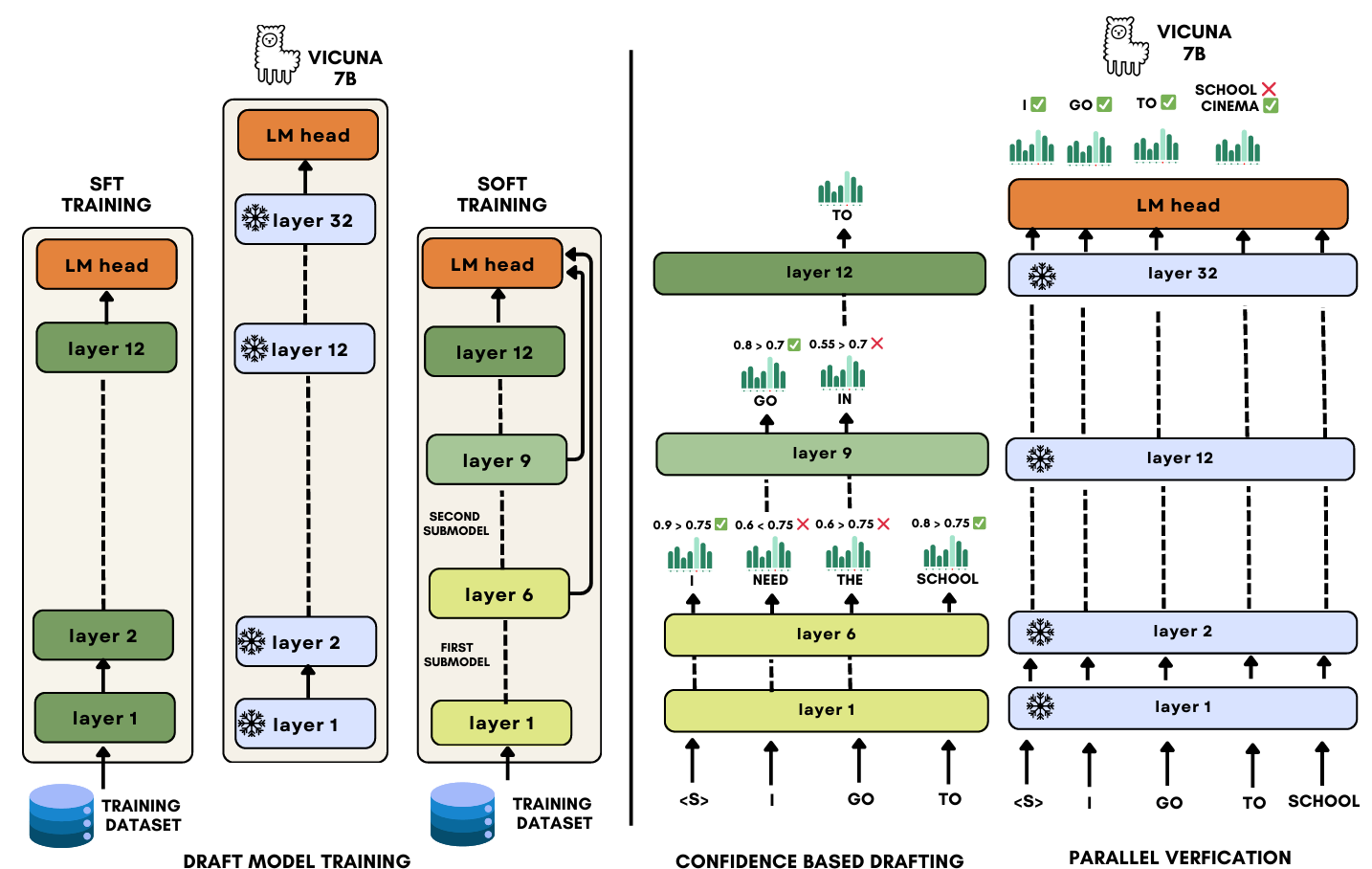 S2D: Sorted Speculative Decoding For More Efficient Deployment of Nested Large Language ModelsParsa Kavehzadeh, Mohammadreza Pourreza, Mojtaba Valipour, and 5 more authors2024
S2D: Sorted Speculative Decoding For More Efficient Deployment of Nested Large Language ModelsParsa Kavehzadeh, Mohammadreza Pourreza, Mojtaba Valipour, and 5 more authors2024Deployment of autoregressive large language models (LLMs) is costly, and as these models increase in size, the associated costs will become even more considerable. Consequently, different methods have been proposed to accelerate the token generation process and reduce costs. Speculative decoding (SD) is among the most promising approaches to speed up the LLM decoding process by verifying multiple tokens in parallel and using an auxiliary smaller draft model to generate the possible tokens. In SD, usually, one draft model is used to serve a specific target model; however, in practice, LLMs are diverse, and we might need to deal with many target models or more than one target model simultaneously. In this scenario, it is not clear which draft model should be used for which target model, and searching among different draft models or training customized draft models can further increase deployment costs. In this paper, we first introduce a novel multi-target scenario for the deployment of draft models for faster inference. Then, we present a novel, more efficient sorted speculative decoding mechanism that outperforms regular baselines in multi-target settings. We evaluated our method on Spec-Bench in different settings, including base models such as Vicuna 7B, 13B, and LLama Chat 70B. Our results suggest that our draft models perform better than baselines for multiple target models at the same time.
-
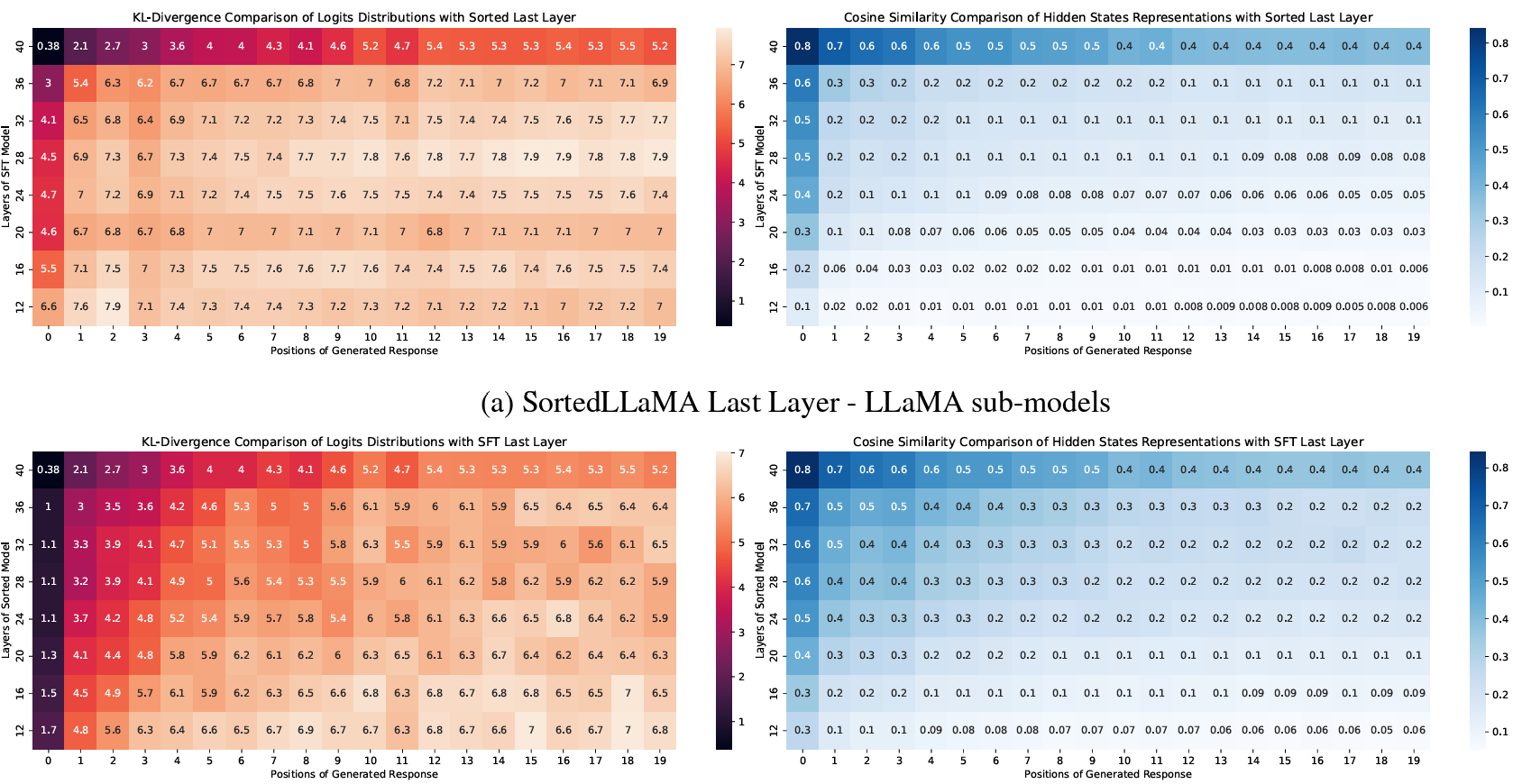 Sorted LLaMA: Unlocking the Potential of Intermediate Layers of Large Language Models for Dynamic InferenceParsa Kavehzadeh, Mojtaba Valipour, Marzieh Tahaei, and 3 more authorsIn Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: EACL 2024, Mar 2024
Sorted LLaMA: Unlocking the Potential of Intermediate Layers of Large Language Models for Dynamic InferenceParsa Kavehzadeh, Mojtaba Valipour, Marzieh Tahaei, and 3 more authorsIn Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: EACL 2024, Mar 2024Large language models (LLMs) have revolutionized natural language processing (NLP) by excelling at understanding and generating human-like text. However, their widespread deployment can be prohibitively expensive. SortedNet is a recent training technique for enabling dynamic inference by leveraging the modularity in networks and sorting sub-models based on computation/accuracy in a nested manner. We extend SortedNet to generative NLP tasks, making large language models dynamic without any Pre-Training and by only replacing Standard Fine-Tuning (SFT) with Sorted Fine-Tuning (SoFT). Our approach boosts model efficiency, eliminating the need for multiple models for various scenarios during inference. We show that this approach can unlock the potential of intermediate layers of transformers in generating the target output. Our sub-models remain integral components of the original model, minimizing storage requirements and transition costs between different computational/latency budgets. The efficacy of our proposed method was demonstrated by applying it to tune LLaMA 2 13B on the Stanford Alpaca dataset for instruction following and TriviaQA for closed-book question answering. Our results show the superior performance of sub-models in comparison to Standard Fine-Tuning and SFT+ICT (Early-Exit), all achieved with very efficient tuning and without additional memory usage during inference.
-
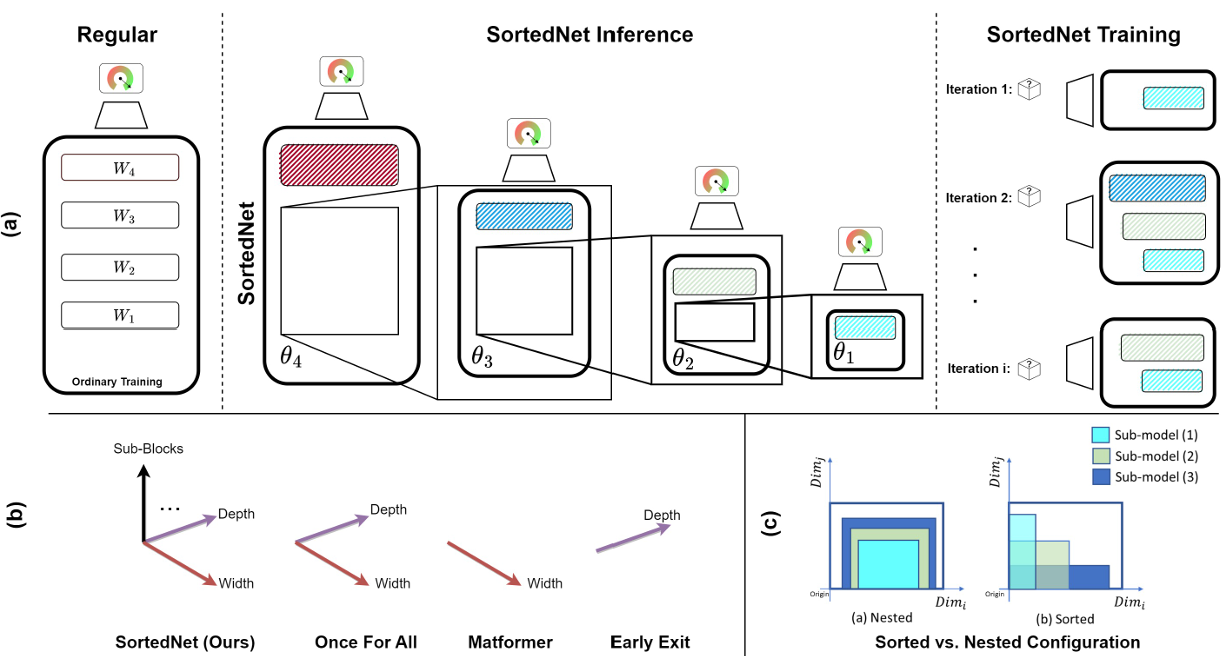 SortedNet: A Scalable and Generalized Framework for Training Modular Deep Neural NetworksMojtaba Valipour, Mehdi Rezagholizadeh, Hossein Rajabzadeh, and 4 more authorsMar 2024
SortedNet: A Scalable and Generalized Framework for Training Modular Deep Neural NetworksMojtaba Valipour, Mehdi Rezagholizadeh, Hossein Rajabzadeh, and 4 more authorsMar 2024Deep neural networks (DNNs) must cater to a variety of users with different performance needs and budgets, leading to the costly practice of training, storing, and maintaining numerous user/task specific models. There are solutions in the literature to deal with single dynamic or many-in-one models instead of many individual networks; however, they suffer from significant drop of performance, lack of generalization across different model architectures or different dimensions (e.g. depth, width, attention blocks), heavy model search requirements during training, and training a limited number of sub-models. To address these limitations, we propose SortedNet, a generalized and scalable training solution to harness the inherent modularity of DNNs. Thanks to a generalized nested architecture (which we refer as sorted architecture in this paper) with shared parameters and its novel update scheme combining random sub-model sampling and a new gradient accumulation mechanism, SortedNet enables the training of sub-models simultaneously along with the training of the main model (without any significant extra training or inference overhead), simplifies dynamic model selection, customizes deployment during inference, and reduces the model storage requirement significantly. The versatility and scalability of SortedNet are validated through various architectures and tasks including LLaMA, BERT, RoBERTa (NLP tasks), ResNet and MobileNet (image classification) demonstrating its superiority over existing dynamic training methods. For example, we introduce a novel adaptive self-speculative approach based on sorted-training to accelerate large language models decoding. Moreover, SortedNet is able to train up to 160 sub-models at once, achieving at least 96% of the original model’s performance.
2023
-
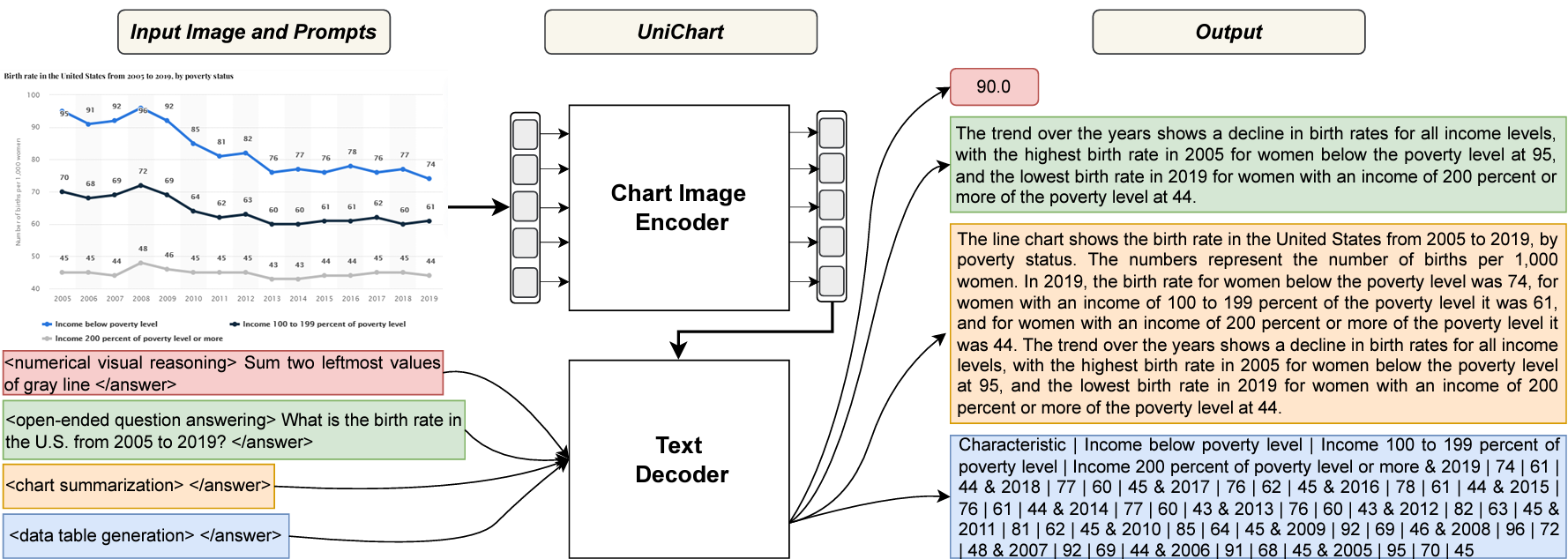 UniChart: A Universal Vision-language Pretrained Model for Chart Comprehension and ReasoningAhmed Masry, Parsa Kavehzadeh, Xuan Long Do, and 2 more authorsIn Proceedings of the 2023 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Dec 2023
UniChart: A Universal Vision-language Pretrained Model for Chart Comprehension and ReasoningAhmed Masry, Parsa Kavehzadeh, Xuan Long Do, and 2 more authorsIn Proceedings of the 2023 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Dec 2023Charts are widely used for data analysis, providing visual representations and insights into complex data. To facilitate chart-based data analysis using natural language, several downstream tasks have been introduced recently such as chart question answering and chart summarization. However, existing methods for these tasks often rely on pretraining on language or vision-language tasks, neglecting the explicit modeling of chart structures (e.g., how chart elements are related to each other). To address this, we first build a large corpus of charts covering diverse topics and visual styles. We then present UniChart, a pretrained model for chart comprehension and reasoning. UniChart encodes the relevant text, data, and visual elements of charts and then uses a chart-grounded text decoder for text generation. We propose several chart-specific pretraining tasks that include: (i) low-level tasks to extract the visual elements (e.g., bars, lines) and data from charts, and (ii) high-level tasks to acquire chart understanding and reasoning skills. Our experiments demonstrate that pretraining UniChart on a large corpus with chart-specific objectives, followed by fine-tuning, yields state-of-the-art performance on four downstream tasks. Moreover, our model exhibits superior generalizability to unseen chart corpus, surpassing previous approaches that lack chart-specific objectives and utilize limited chart resources.
-
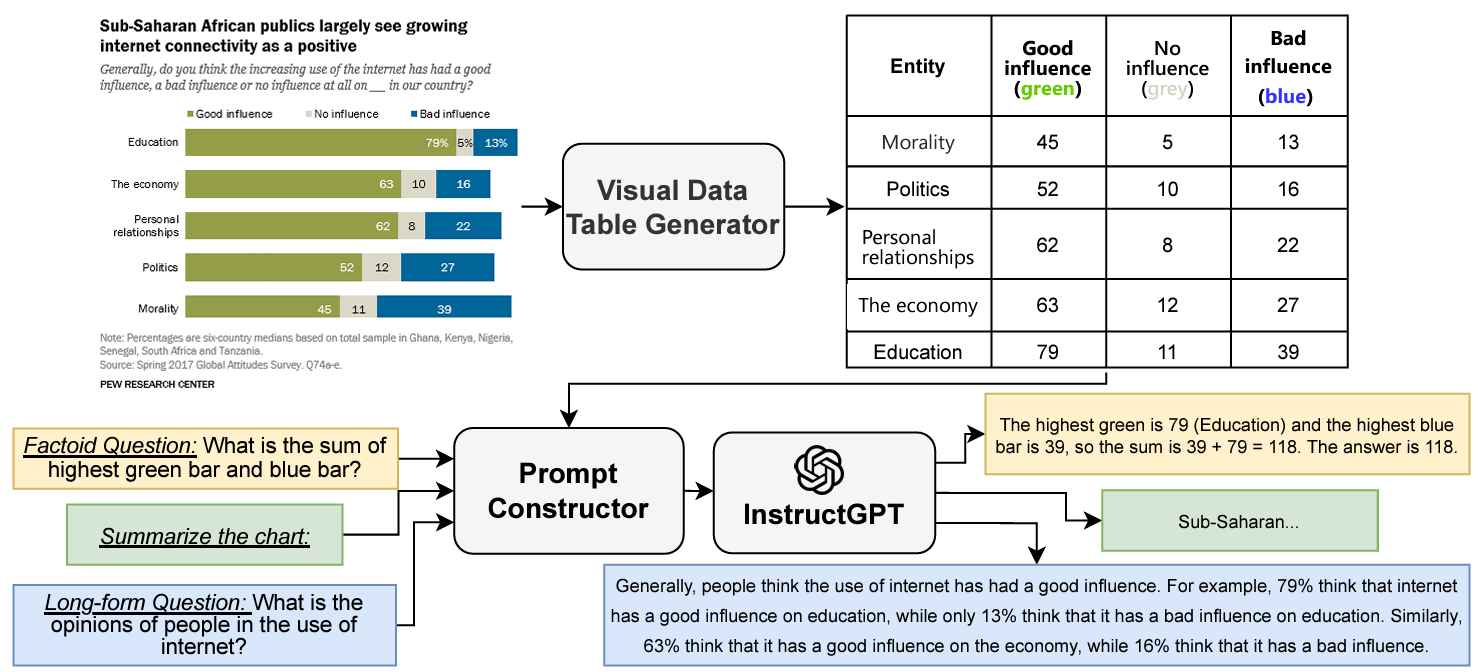 Do LLMs Work on Charts? Designing Few-Shot Prompts for Chart Question Answering and SummarizationXuan Long Do, Mohammad Hassanpour, Ahmed Masry, and 3 more authorsDec 2023
Do LLMs Work on Charts? Designing Few-Shot Prompts for Chart Question Answering and SummarizationXuan Long Do, Mohammad Hassanpour, Ahmed Masry, and 3 more authorsDec 2023A number of tasks have been proposed recently to facilitate easy access to charts such as chart QA and summarization. The dominant paradigm to solve these tasks has been to fine-tune a pretrained model on the task data. However, this approach is not only expensive but also not generalizable to unseen tasks. On the other hand, large language models (LLMs) have shown impressive generalization capabilities to unseen tasks with zero- or few-shot prompting. However, their application to chart-related tasks is not trivial as these tasks typically involve considering not only the underlying data but also the visual features in the chart image. We propose PromptChart, a multimodal few-shot prompting framework with LLMs for chart-related applications. By analyzing the tasks carefully, we have come up with a set of prompting guidelines for each task to elicit the best few-shot performance from LLMs. We further propose a strategy to inject visual information into the prompts. Our experiments on three different chart-related information consumption tasks show that with properly designed prompts LLMs can excel on the benchmarks, achieving state-of-the-art.
2022
-
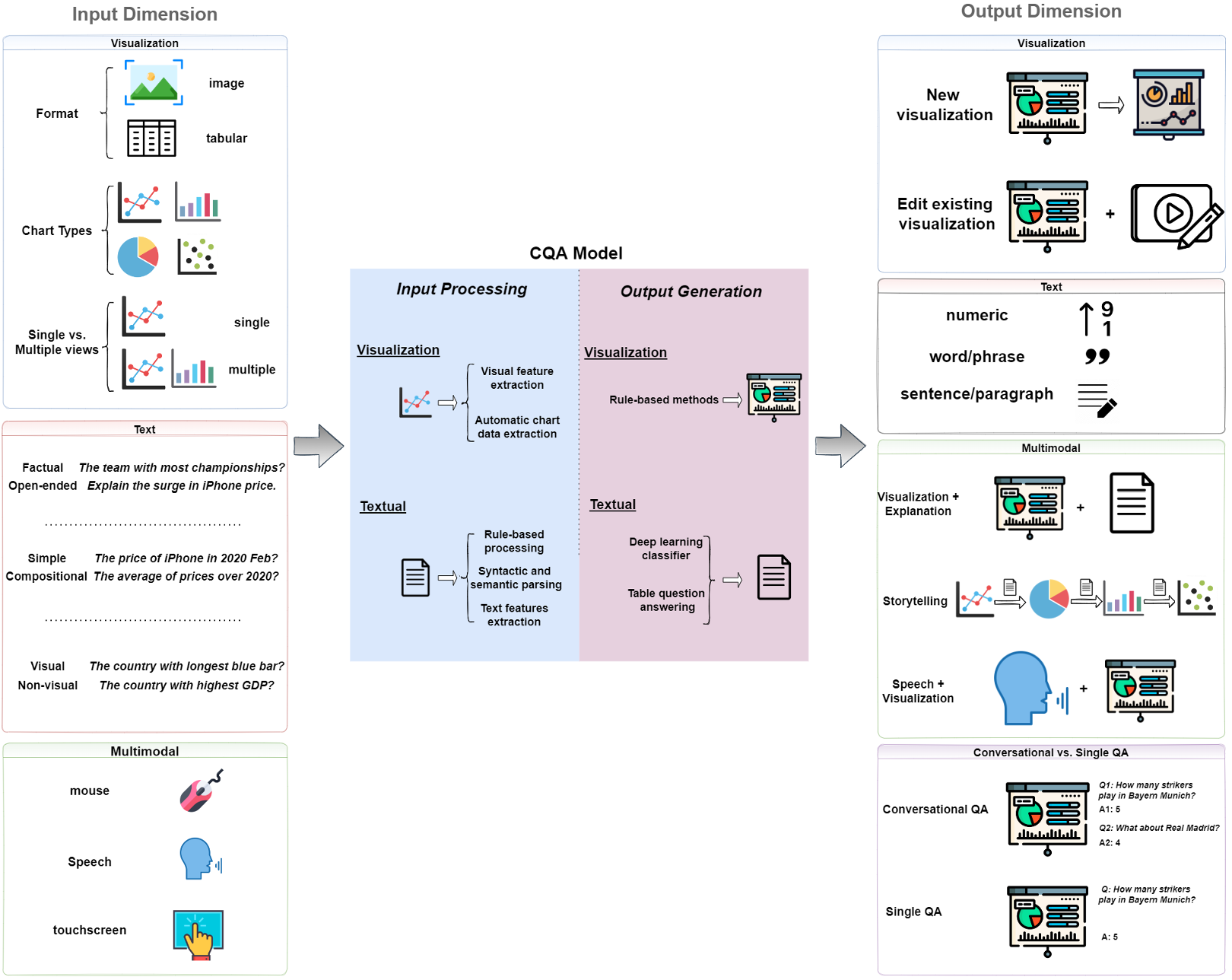 Chart Question Answering: State of the Art and Future DirectionsEnamul Hoque, Parsa Kavehzadeh, and Ahmed MasryDec 2022
Chart Question Answering: State of the Art and Future DirectionsEnamul Hoque, Parsa Kavehzadeh, and Ahmed MasryDec 2022Information visualizations such as bar charts and line charts are very common for analyzing data and discovering critical insights. Often people analyze charts to answer questions that they have in mind. Answering such questions can be challenging as they often require a significant amount of perceptual and cognitive effort. Chart Question Answering (CQA) systems typically take a chart and a natural language question as input and automatically generate the answer to facilitate visual data analysis. Over the last few years, there has been a growing body of literature on the task of CQA. In this survey, we systematically review the current state-of-the-art research focusing on the problem of chart question answering. We provide a taxonomy by identifying several important dimensions of the problem domain including possible inputs and outputs of the task and discuss the advantages and limitations of proposed solutions. We then summarize various evaluation techniques used in the surveyed papers. Finally, we outline the open challenges and future research opportunities related to chart question answering.
2021
-
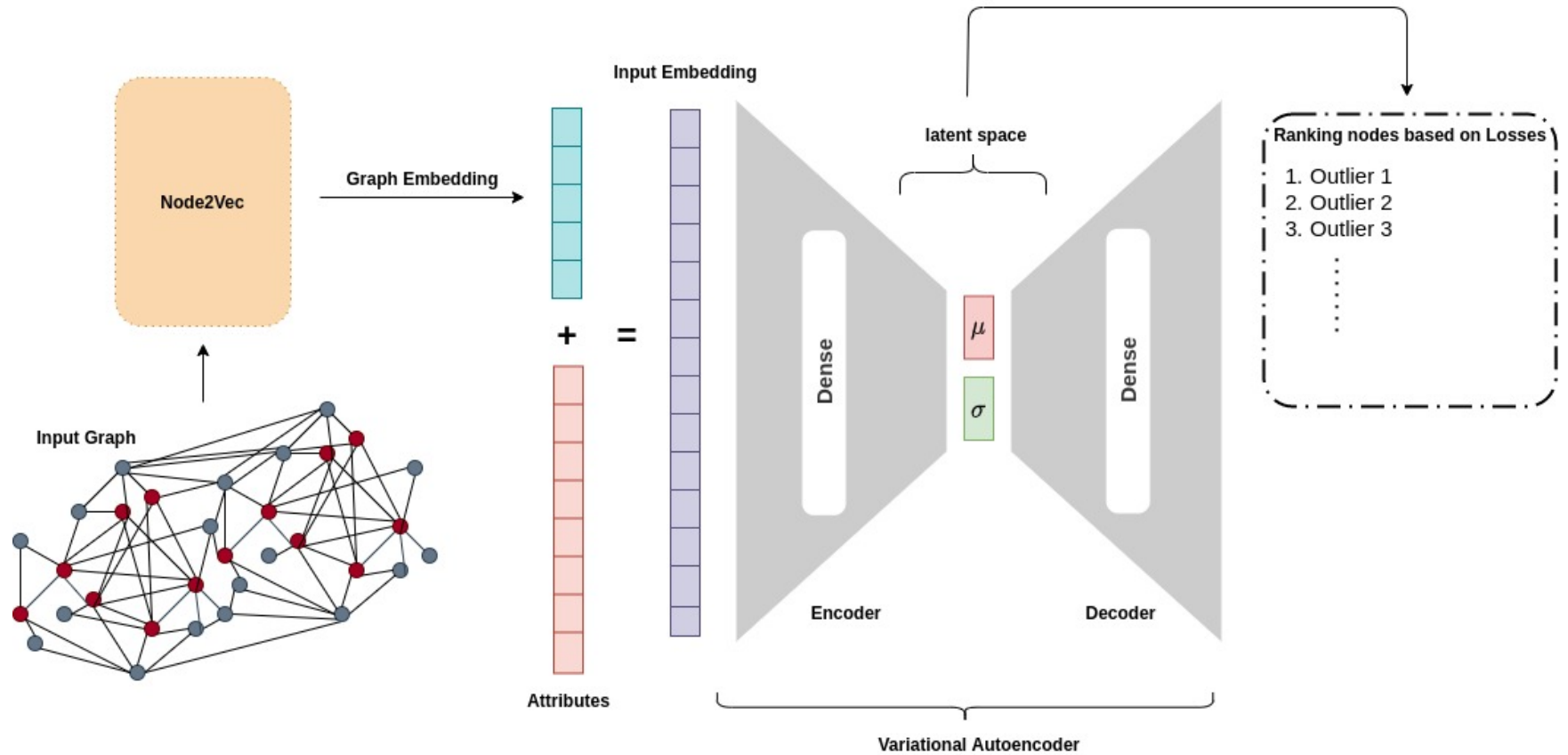 Unsupervised Anomaly Detection on Node Attributed Networks: A Deep Learning ApproachParsa Kavehzadeh, Mohammadreza Samadi, and Maryam Amir HaeriIn Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Information Science and Systems, Edinburgh, United Kingdom, Dec 2021
Unsupervised Anomaly Detection on Node Attributed Networks: A Deep Learning ApproachParsa Kavehzadeh, Mohammadreza Samadi, and Maryam Amir HaeriIn Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Information Science and Systems, Edinburgh, United Kingdom, Dec 2021Anomaly detection has been one of the important issues in social network analysis in recent years due to the crucial role it plays in different applications such as fraud and spammer detection. Using both graph and node characteristics leads to more accurate results in detecting anomalous nodes of node attributed networks. Most of the research works in this field are concentrated on supervised methods for anomaly detection. However, in real-world problems, there is not enough labeled data to use supervised methods for anomaly detection. This paper proposes an unsupervised method for detecting anomalous nodes in node attributed networks. The methods used a two-step deep learning approach. In the first step, structural features of the network are extracted using node2vec; in the next step, Variational AutoEncoder (VAE) is used to detect the anomalies considering both structural and node attributes. The anomalous nodes are recognized by their higher reconstruction loss. Our experimental results on two datasets, BlogCatalog and Flickr, show that the suggested method can compete with the state-of-the-art approaches of anomaly detection in attributed networks. Our method (Deep2NAD) outperforms the state-of-the-art result on the Flickr dataset based on AUC. Moreover, it receives an acceptable AUC over the BlogCatalog dataset in comparison to the state-of-the-art methods.